Mangroves are ecosystems located in intertidal areas, namely areas along the coastline or the banks of rivers where strong interactions occur between marine, brackish, river, and terrestrial. Mangrove ecosystems are found in shallow bay beaches, estuaries, deltas, and protected coastal areas. Mangroves can be a good ecosystem if they are supported by three main conditions: brackish water, calm water flow, and relatively flat mud deposits. Mangroves live in the tropics and subtropics, especially at 25° North Latitude and 25° South Latitude.
Plants in mangrove ecosystem generally have certain morphological forms and physiological mechanisms as an adaptation of mangrove environment. The adaptation is related to reproductive system (propagul), loose and anoxic (anaerobic) soil, and high salinity. Mangrove plants are divided into three groups: major mangrove (Avicennia sp., Rhizophora sp.), minor mangrove (Excoecaria sp., Xylocarpus sp.), and associated mangrove (Pandanus sp., Acathus sp.).
Indonesia has ± 202 species of mangroves, including 89 species of trees, 5 species of palms, 19 species of lianas, 44 species of soil herbs, 44 species of epiphytes, and 1 species of fern. The most common types of mangroves found are bakau (Rhizhopora sp.), api-api (Avicennia sp.), bogem or pedada (Sonneratia sp.), and tancang (Bruguiera sp.).
Badak LNG has a mangrove conservation area located in Berbas Tengah which functioned as a buffer zone area. The composition of mangrove vegetation was dominated by Rhizophora apiculata Blume from Rhizophoraceae family. Rhizophora apiculata is also known as oil mangrove. Rhizophora apiculata is fast-growing mangroves with hard wood, breath roots, opposite leaf types, and could reaches 15 meters high. Rhizophora apiculata has many benefits: the wood is used for building materials, firewood, and charcoal, the root branches can be used as anchors, and the bark contains up to 30% tannins (percent dry weight) as dyes and adhesives.

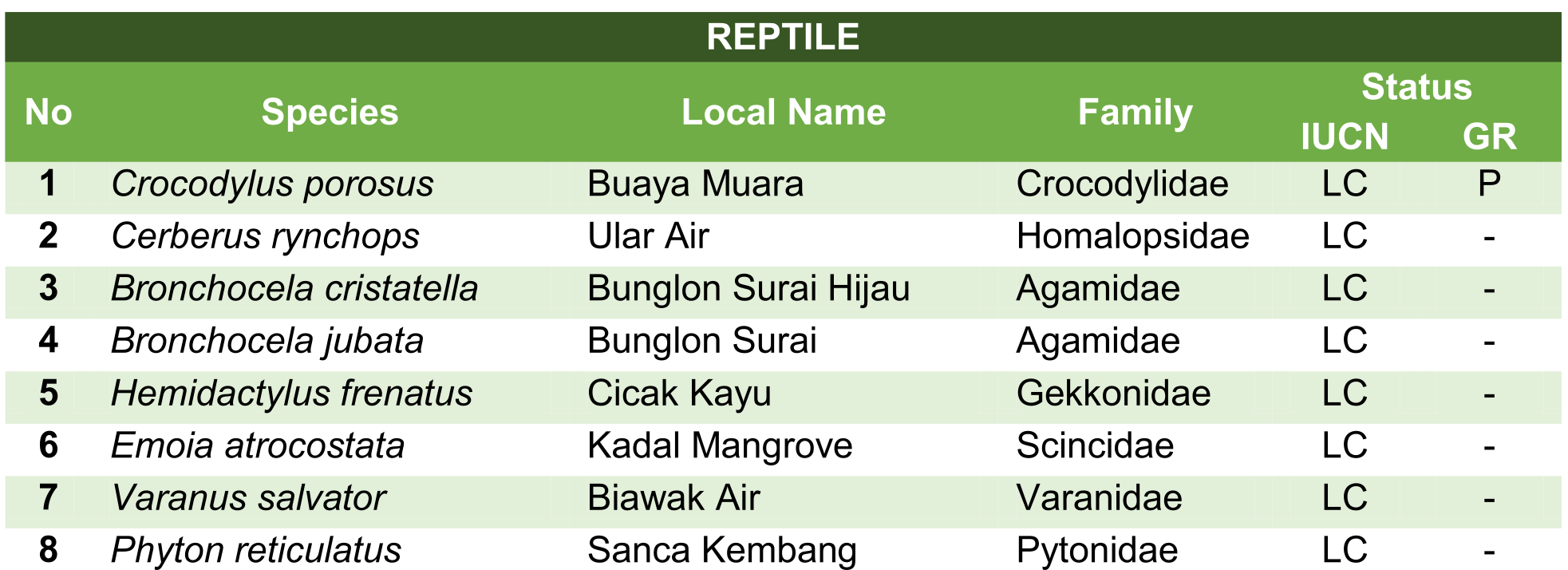
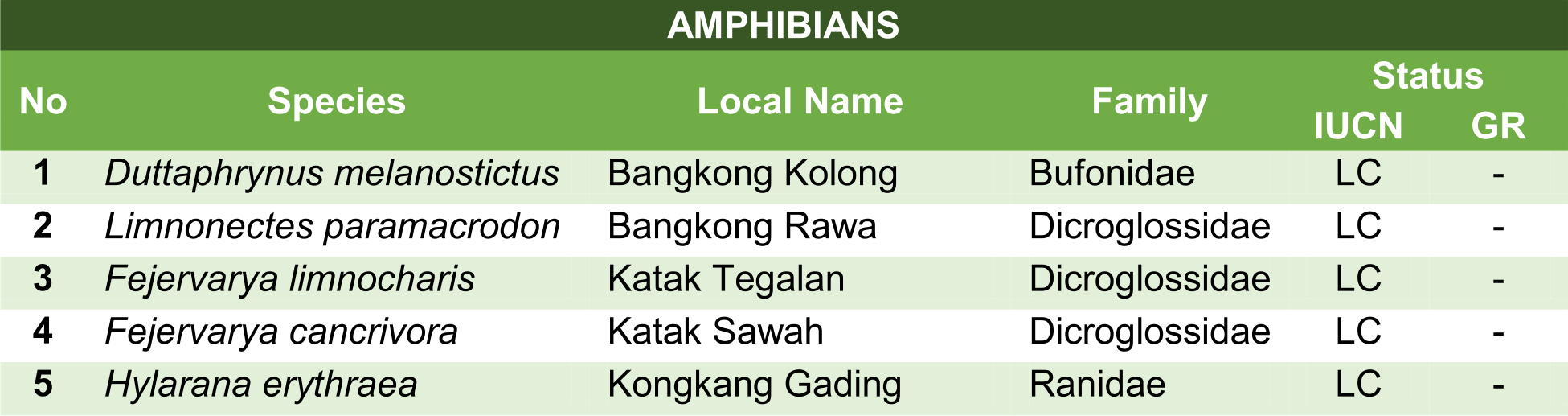
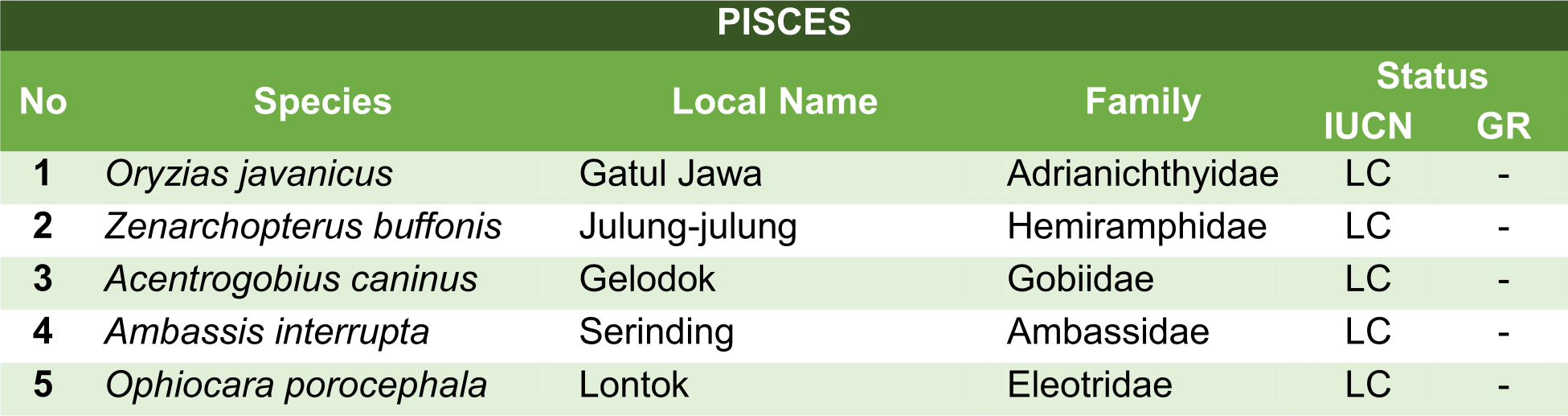
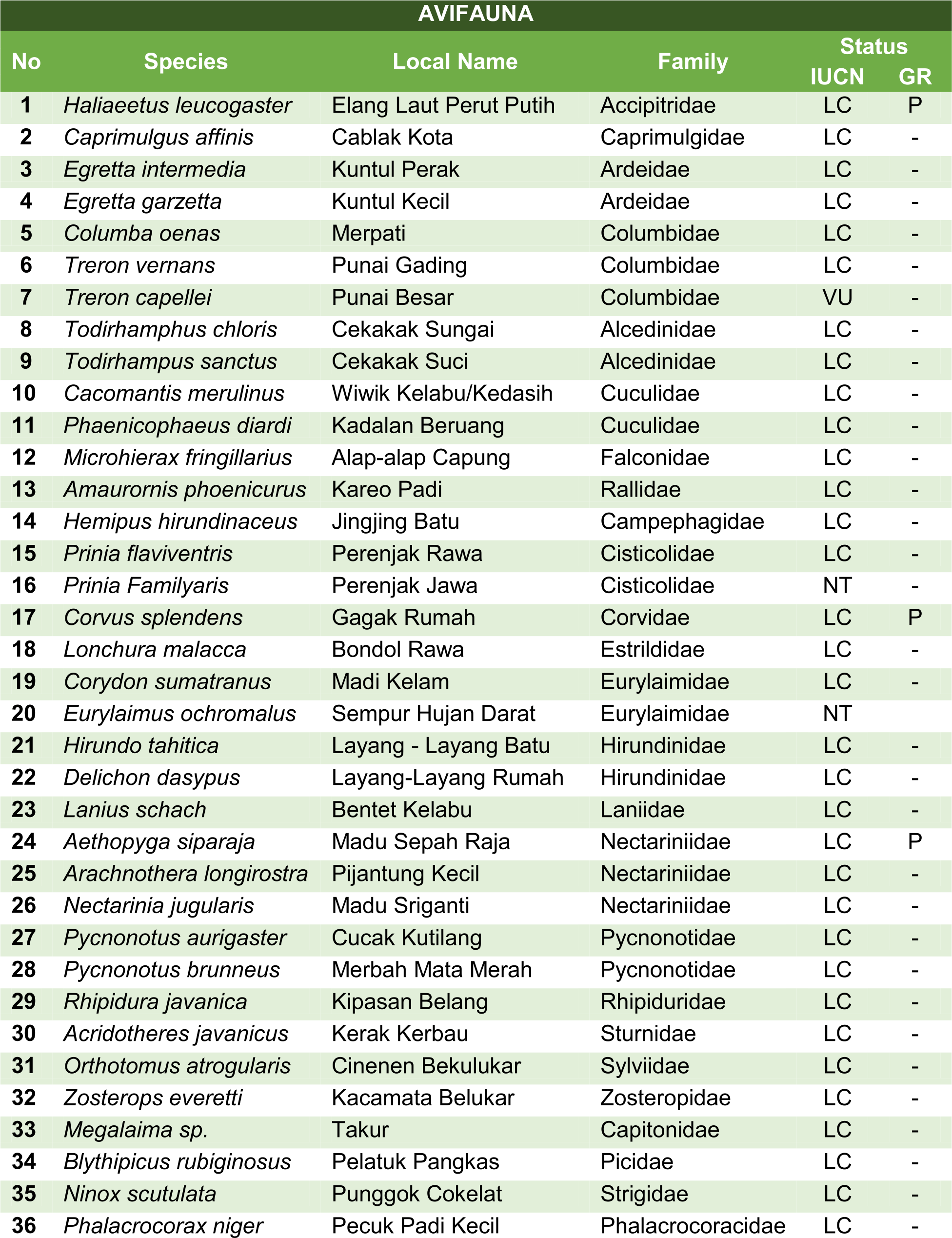
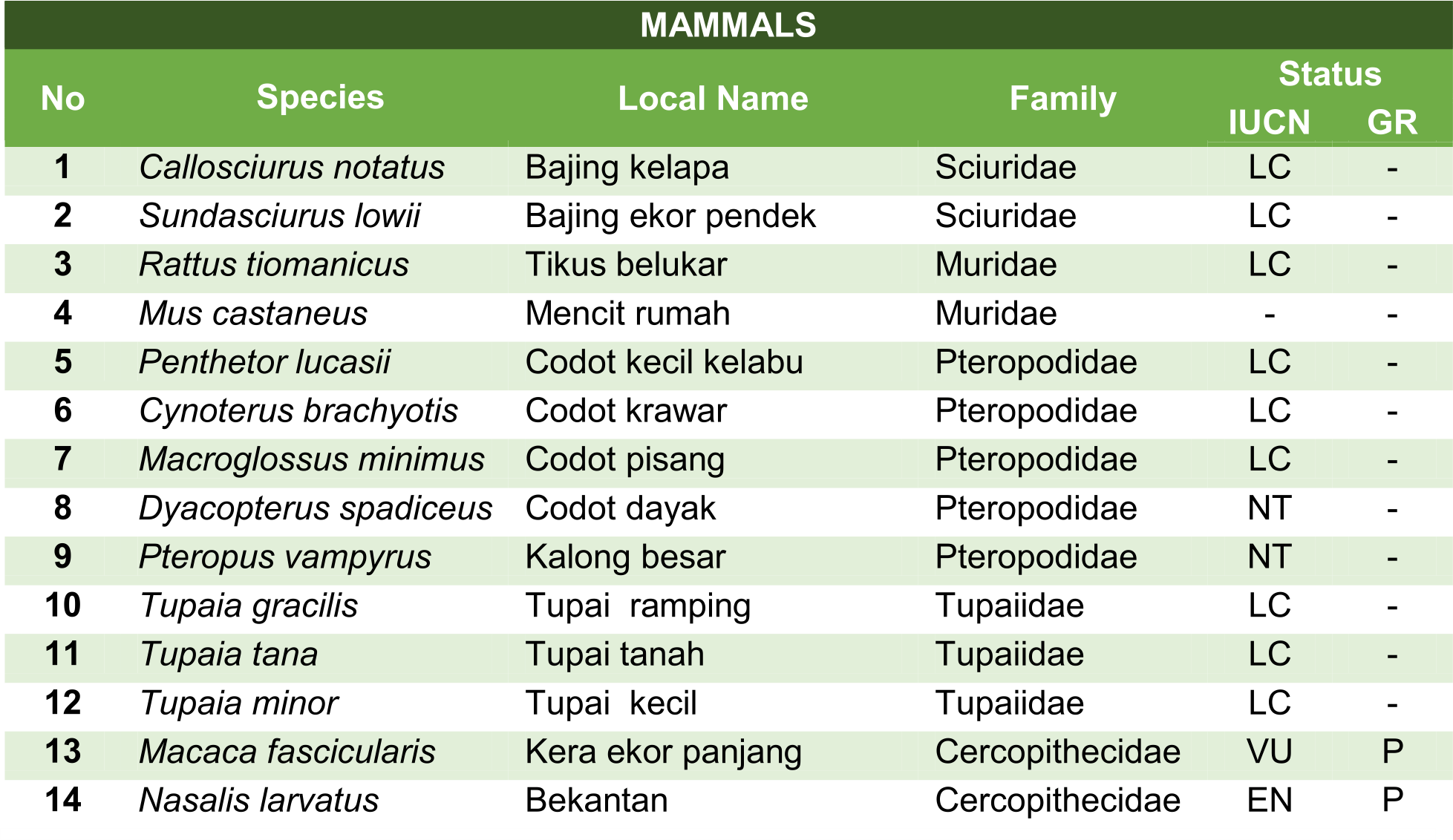
Here are some of the animals which can be found in Badak LNG's mangrove area: